Urinary Tract Infections in Women
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among one of the most common reasons women visit their doctor’s office. At least 50 percent of women will experience at least one symptomatic urinary tract infection during their lifetime. While some UTIs are solitary events, most women experience multiple infections. There isn’t a week that goes by at Pacific Coast Urology Medical Center that we don’t see many new female patients needing to be evaluated for UTIs.
WHY ARE UTIS SO MUCH MORE COMMON IN WOMEN THAN MEN?
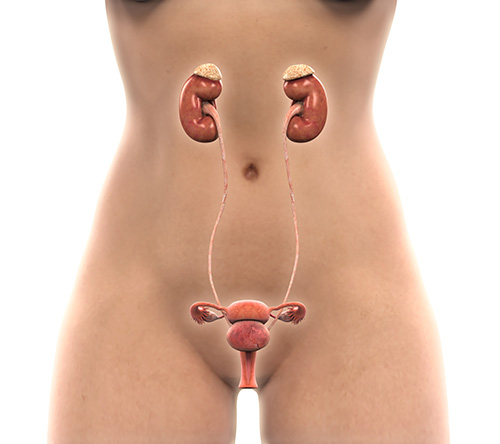
It’s an issue of anatomy. The female urethra is short – just a few centimeters in length. That length means it’s just a short distance that bacteria have to travel from the end of the female urethra (where they are always plentiful) to the bladder.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS?
There are two basic types of UTIs: (1) uncomplicated and (2) complicated.
Examples of uncomplicated UTIs are:
- Certain physical activities make the bacteria more likely to travel – sexual intercourse is one of them. That’s why it’s important to keep the vaginal area as clean as possible before sexual activity and to make sure your partner is clean, too.
- Age is a factor in UTI development. At younger ages, the pH of the vagina changes, making UTIs more likely. Decades later, as menopause starts and estrogen levels decrease, vaginal and urethral tissues dry and contract, potentially causing a restriction in urine flow and incomplete bladder emptying. That sets the stage for UTI development.
- Perhaps the most common cause of UTIs in women is inadequate fluid consumption. Drinking enough fluid makes you urinate more and urinating is the natural way to cleanse bacteria from your urethra.
Examples of complicated UTIs are:
Complicated UTIs are just that – complicated! That means that there are underlying circumstances that make UTI development more likely. Here are some examples:
- Diabetes. This can cause multiple problems including a generalized increase in susceptibility to infections and a weakened bladder muscle that prevents bladder emptying.
- Bladder stones. They develop when bladders do not empty completely and can grow as large as an egg. They have the ability to trap bacteria and are a constant source of infections.
- Overactive bladders. When bladders contract abnormally and cause urine leakage, that can be a never ending source of infection.
TO LEARN MORE ABOUT OVERACTIVE BLADDERS CLICK HERE
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF A URINARY TRACT INFECTION?
With a urinary tract infection (UTI) the lining of the bladder and urethra become irritated. It is this irritation that causes pain in your lower abdomen and pelvic area. It also causes abnormal function of the bladder muscle, causing urinary frequency, emptying only small amounts and a sensation of incomplete emptying. Other symptoms include burning when you urinate, cloudy urine and an unpleasant urine smell. In severe infections, you might have blood in your urine.
Some UTIs ascend from the bladder to the kidneys. This poses a serious health problem. Kidney infections can be life threatening. They are usually associated with a fiver and back pain. So, if you have UTI symptoms, back pain and a fever, it’s a good idea to head to the closest hospital emergency department to make see if you have a kidney infection.
HOW ARE URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS DIAGNOSED?
At Pacific Coast Urology Medical Center we diagnose a UTI by doing a routine urinalysis. Well, routine by our standards. We take your urine sample, put it in a high speed centrifuge and then examine what’s left under a microscope. Other offices, and most urgent care centers, cannot do this. We’re able to know immediately if there are bacteria and white blood cells in your urine. Most importantly, we can often determine the likely type of infection so you can start taking the correct antibiotic right away!
LEARN MORE:
ACCURACY OF ONLINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS FOR URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS …WHAT ARE THE TELEHEALTH LIMITATIONS? READ DR. PUGACH’S BLOG
HOW ARE URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS TREATED? (READ UTI TREATMENT & PREVENTION)
Don’t delay treatment if you suspect you have a urinary tract infection. If you do have one, we’ll treat it and find out why it happened. We’re here to keep you healthy!
Call, Pacific Coast Urology Medical Center at 888-7354336 or email us via our Contact Us Form.